Table of Contents
Blended Finance Meaning
Blended finance is an innovative approach to finance that uses development finance and lets investors choose their risk tolerances. It aids in mobilizing surplus funds to developing countries to encourage sustainable development and is an effective method for funding crucial, challenging projects.
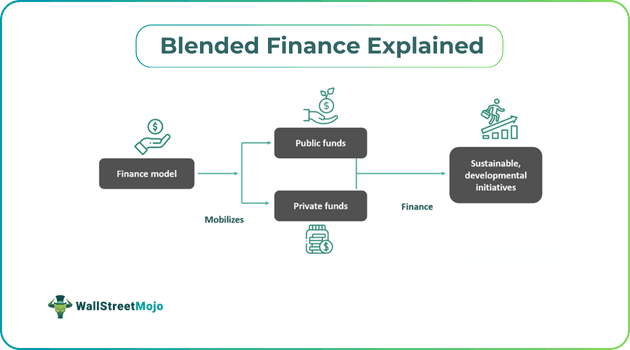
The financing method offers an opportunity to blend government funding, private sector investing and philanthropy for sustainable development initiatives. It facilitates financing projects that have huge impacts on green, social and sustainability. It helps developing nations and least developed nations receive sustainable finance that can affect social and environmental issues.
Key Takeaways
- Blended finance is an approach to finance that makes use of development finance and aids in the mobilization of surplus funds for encouraging sustainable development.
- It is an effective method for funding crucial, challenging projects, especially in developing countries.
- Private funding under this can accommodate investors with various risks and return expectations.
- It combines private and public funding, hence providing a structured approach to funding.
- It also promotes investments in sustainable initiatives, helps developing countries and finds equitable solutions to the economies.
How Does Blended Finance Work?
Blended finance, as defined by the UN, is a method that combines concessional government financing and nonconcessional private finance with knowledge from the private and public sectors. The OECD, or the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, looks at it more broadly. The OECD describes it as an efficient use of developmental finance to mobilize surplus funds toward sustainable developmental goals for developing nations.
The financing method has three major features: leverage, impact and returns. It leverages the use of a developmental and philanthropic nature to engage and mobilize private capital. The financing method aims to make economic, environmental and social impacts. Furthermore, it also aims to acquire risk-adjusted market-based returns for investors.
Under this, investors forage into long-term and large-scale capital development projects for better returns and to fund crucial development needs. They are classified as institutional investors and concessionary investors. Institutional investors invest their funds majorly in the required capital and usually invest for returns that are profitable and risk-adjusted. They include asset managers, bankers and insurers. etc. concessionary investors are investors who invest relatively less amount but are willing to incur less than market rate returns and higher risk tolerance. There are intermediaries under this arrangement. These intermediaries work to match investments made for funding to the projects. They consist of subject matter experts in finance and are often sponsored by private institutions and development banks. After the allocation, the projects receive their respective funding.
Funding generally focuses on working with Blended finance principles. Concessional finance, commercial sustainability, crowding-in and minimum concessionality, promoting high standards and reinforcing markets are termed the blended finance principles.
When To Use Which Instrument?
Investors apart from the broader market bonds have options for thematic bonds such as GSS (Green, social and sustainability) bonds and SLBs (Sustainability-linked bonds). Investors interested in achieving ESG impact and contributing to the developmental objectives to diversify their portfolios can opt for GSSS (Green, social, sustainability and sustainability-linked) bonds. They are also provided an opportunity to portray shareholder interests. GSSS bond assessments can be complex.
On the other hand, SLBs advance the development of sustainable investment options. They are flexible, provide incentives for positive outcomes, and have larger tenors than GSS bonds. They can exceed the given issue size, and investors who opt for these factors can opt for SLB bonds.
Regardless of desired factors, investors must consider certain common factors. These factors involve credit risks such as debt default risks, political risks, liquidity risks and currency risks.
These factors have to be considered when the private sector bids prices at auctions. It is the sovereign issuer who has a higher credit rating that will bring a low interest rate. The investors who chose low credit rating bonds will have to bear additional risk for earning higher returns.
Examples
Let us look into some examples to understand the concept better
Example #1 - A hypothetical example of blended finance models
Let us take a hypothetical example of XYZ Power Finance Corporation, a public sector unit in the country" A" (another hypothetical element). The corporation wants to make a positive environmental impact and reduce the existing use of fossil fuels. In an attempt to foster climate-resilient, low-carbon development, it took the opportunity to partner with Country A's blended finance facility that it set up with the World Bank. An agreement that focused on funding climate projects was signed between XYZ and country A. under the agreement. XYZ will finance the projects, and Country A's government will facilitate the implementation of projects signed as per the terms.
Example #2 - A real-life example of blended finance models
In 2023, the United States Agency for International Development, USAID, and the U.S. Department of State launched the BFET or the blended finance for energy transition program. It aims to mobilize $1 billion of funding to develop energy transition efforts in emerging markets. The ultimate goal is environmental sustainability and works towards contribution of limiting average global temperature rise to 1.5°C.
Importance
Given below are some of the points of import for the financing method:
- Structured approach - The financing technique allows organizations with varied interests to come together for individual and common achievement of objectives. It gives an opportunity for investors to achieve good returns and make a social impact at the same time through investment options in bonds, etc.
- Promotes investment in sustainable initiatives - Ambitious projects are coming up in various fields due to developments taking place across the world. Advancements along with sustainability are the key to efficient growth in today's times. The blended financing method promotes such initiatives.
- Focus on developing countries - Equity in developments is a fueling factor in blended financing. The growth of developing countries depends on advancements in varied aspects such as poverty alleviation, sanitation, clean drinking water and physical infrastructure. The financing method creates investment opportunities in such economies.
- Equitable solutions - Blending public and private sources of funding ensures accountability and profitability. Commercial development projects bring development and profit into the equation and aid in the promotion of welfare along with monetary gains.
